What is CRISPR?
Intellia is currently investigating CRISPRAdapted from a naturally occurring bacterial immune system, CRISPR is an acronym for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. One of the proteins in the CRISPR system is known as CRISPR-associated 9 protein or Cas9 protein, which acts as a pair of ‘molecular scissors’ to cleave DNA. Researchers have co-opted the bacterial CRISPR system to make specific changes in the DNA of humans, other animals and plants. CRISPR was first harnessed in 2012 as a genome editing tool in the lab. More recently, scientists have begun engineering and testing CRISPR systems to be very specific to a desired genetic target. for gene editingAlso called gene editing. Genome editing collectively refers to a set of technologies, including CRISPR/Cas9, that can be used to cut and modify DNA. Genome editing uses systems to make the DNA change inside the cell. These cells can be edited in the body (in vivo) or outside the body (ex vivo) from a patient or donor., a new way to make changes to DNAAcronym for deoxyribonucleic acid, the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and contains the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. to potentially treat genetic disease.
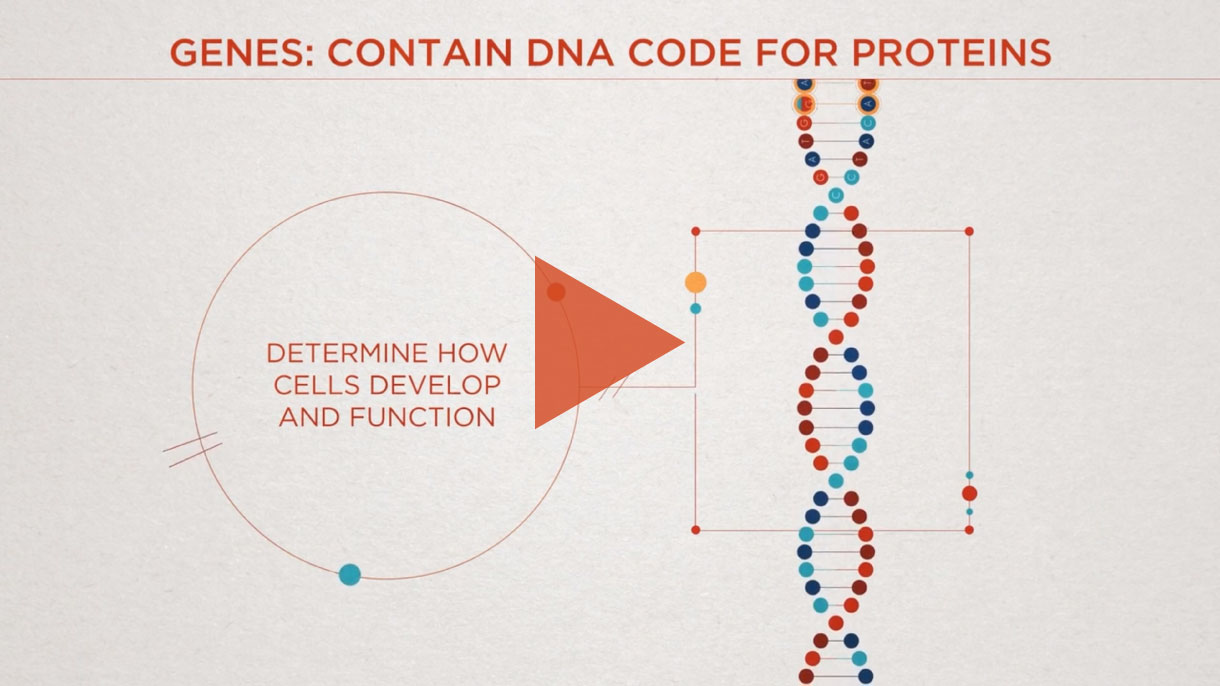
Your genomeA genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. In humans, a copy of the entire genome—more than three billion DNA base pairs—is contained in all cells that have a nucleus. is your entire collection of genes that contain the DNA code for making proteins. Gene editing refers to a set of technologies, including CRISPR, which can be used to make DNA changes inside a cell. These cells can be edited inside the body (in vivoMeaning “within the living”, this type of therapy is administered directly into the patient, targeting the cells and editing the genome from inside the body.) or outside the body (ex vivoAlso referred to as a cell therapy. In an ex vivo therapy, cells are removed from the body for modification. Modification is done by administering therapy directly to the cells before they are returned to the body. In the case of ex vivo CRISPR/Cas9 therapies, CRISPR/Cas9 is used to modify cells to repair them to their desired functions. The engineered cells are then administered to the patient so they can treat a particular disease.) from a patient or donor.
Adapted from a naturally occurring bacterial immune system, CRISPR, an acronym for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, allows scientists to harness the power of natural DNA repairCorrection of “misspelled” disease-driving DNA sequence using a CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing therapy. mechanisms
In the future, Intellia hopes to use its CRISPR technology to treat a variety of human diseases.

Types of Edits
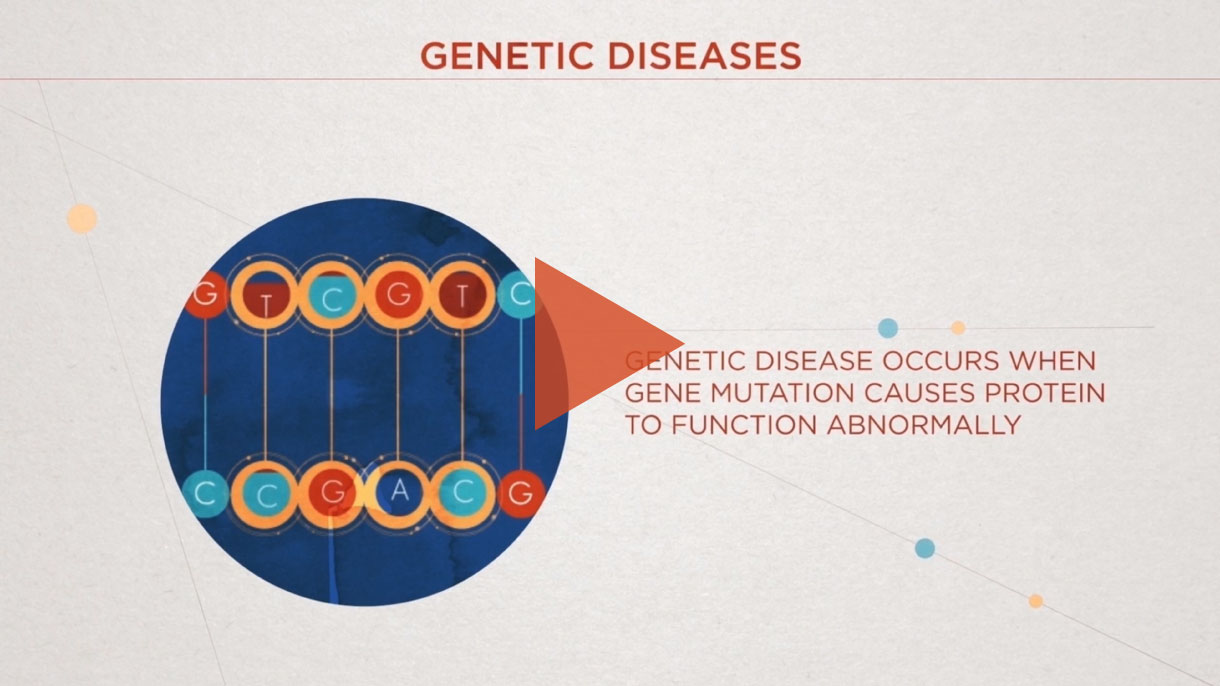
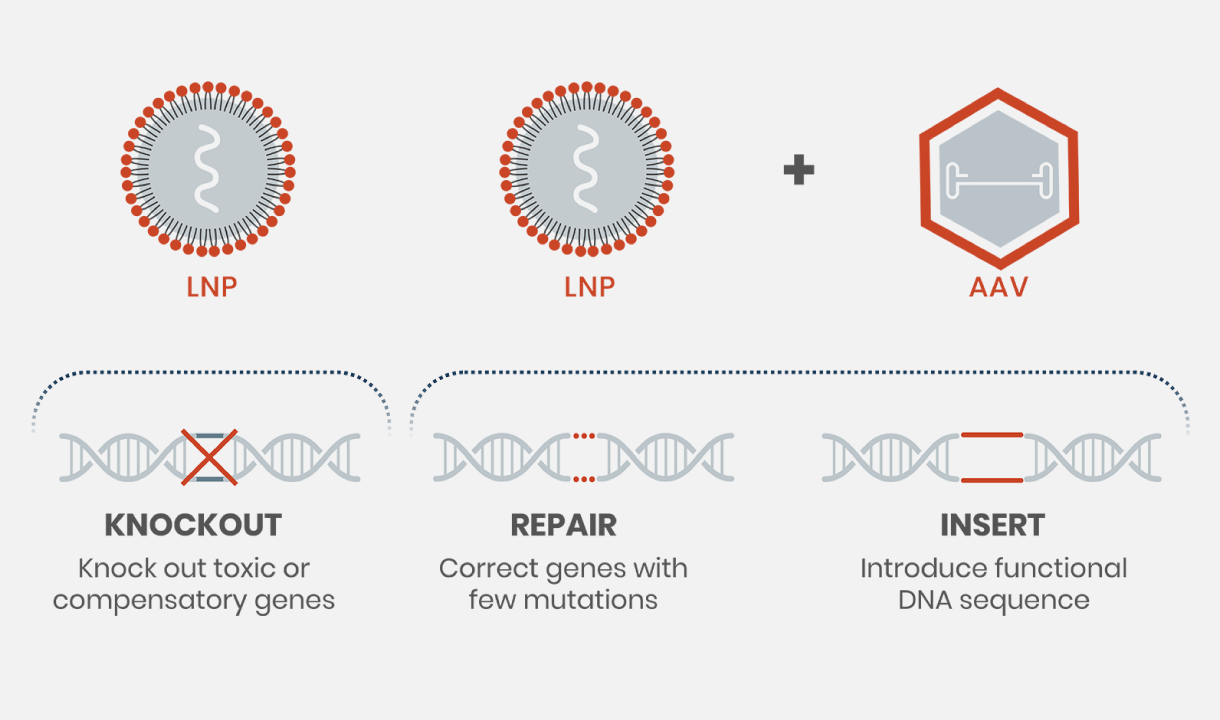
Genetically driven diseases, caused by mutations (a change in the DNA sequence), come in many different forms. Intellia is applying and optimizing its CRISPR genome editing platform to address each of these types of mutations.
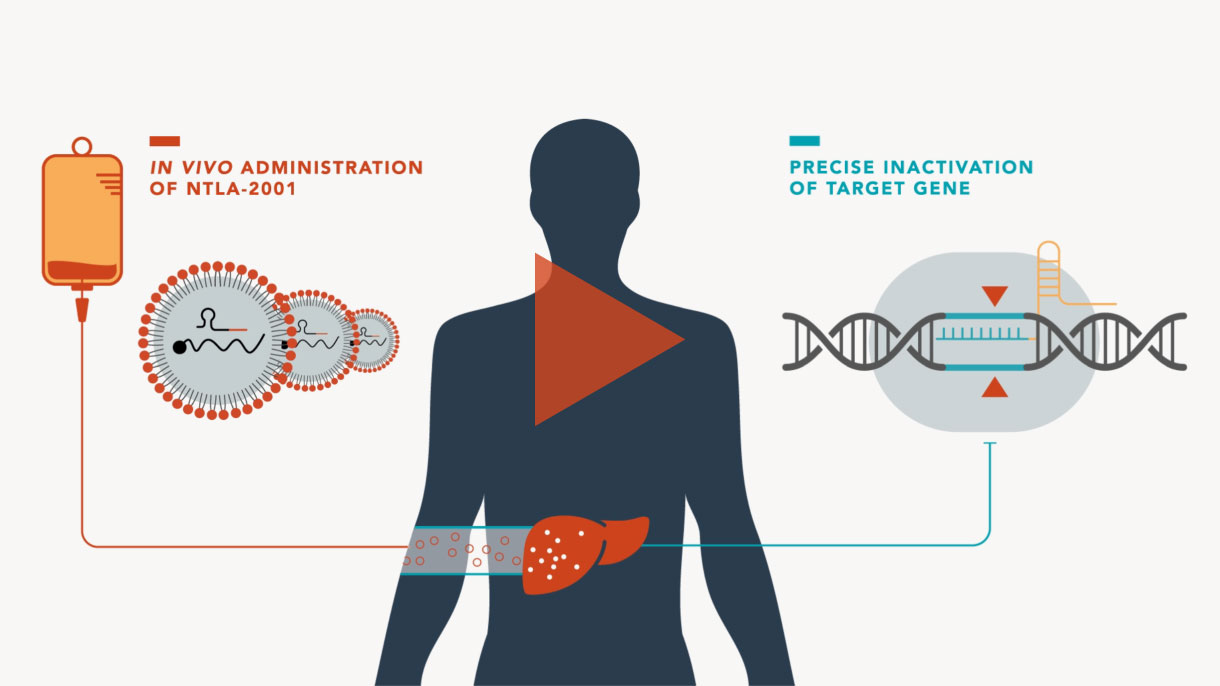
In Vivo
CRISPR is the therapy
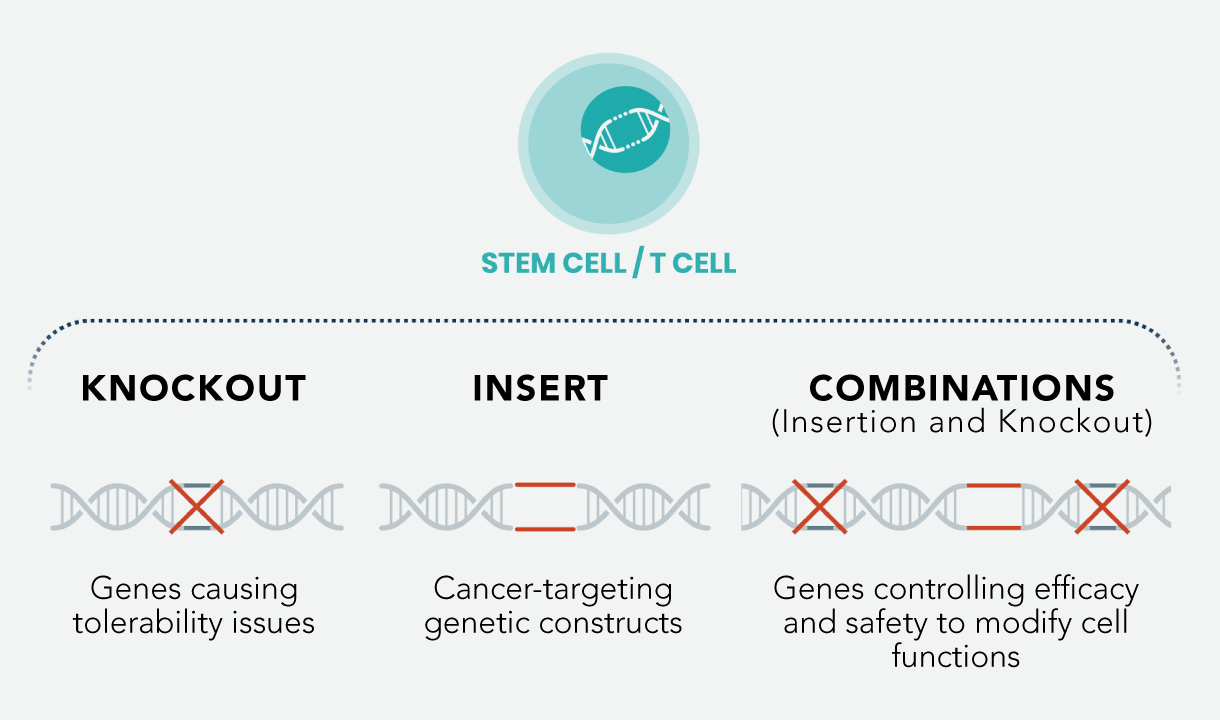
Our systemic lipid nanoparticleAlso known as LNP. LNPs are fat-based molecules that are the basis of Intellia’s CRISPR/Cas9 delivery platform. In Intellia’s experimental treatments, an LNP delivers to its target gene a simple, two-part genome editing system: the messenger RNA that encodes the Cas9 protein and the guide RNA that can target a specific DNA sequence. (LNP)-based delivery system has unlocked treatment of genetic diseases to both selectively knock out disease-causing genes and restore necessary genetic functions by targeted insertionInsertion of a new DNA sequence into the genome to manufacture a desired protein using a gene editing technology, such as the CRISPR/Cas9 system..
Ex Vivo
CRISPR creates the therapy
We are focused on engineering T cellType of white blood cell, or leukocyte, essential to the immune system. Intellia is engineering T cells against specific cancer antigens. therapies to provide them with particular enhanced attributes that may enable them to more effectively treat oncological and immunological diseases. Our approach is designed to improve safety and efficacy by engineering cell therapiesType of therapy where engineered cells are transferred into a patient’s body to grow, replace or repair damaged tissue, or perform another desired function. Cells used in these therapies may originate from a healthy donor (allogeneic cells). A common type of cell therapy is blood transfusions, where red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets from one or more donors are transferred into the body of a patient. that are more precise, potent and persistent.